What is an ECS mandate? In an era of digital payments and automatic bill settlements, the ECS mandate is a widely used tool that makes recurring payments more convenient and reliable. Whether it’s utility bills, loan EMIs, insurance premiums, or subscription fees, an ECS mandate helps ensure timely payments without manual intervention.
This guide explains what an ECS mandate is, how it works, the different types, its benefits, and how it compares to newer systems like NACH. If you’ve ever wondered how an ECS payment mandate works, this article simplifies everything for you.
What Does “ECS Mandate” Mean?
ECS stands for Electronic Clearing Service. An ECS mandate is a formal authorisation given by a bank account holder to a service provider or bank, allowing automatic deduction of specific amounts from their account at predetermined intervals.
It’s essentially a permission slip that lets companies collect payments from your bank account without requiring you to initiate the transaction each time.
This electronic process replaced slow manual bank transfers and has been widely used in India for recurring payments.
How ECS Mandate Works
Here’s how the ECS mandate process generally works:
- Mandate Setup:
You provide an ECS mandate to the service provider or biller, usually by signing a physical form or completing a digital form. - Verification by Bank:
Your bank verifies the mandate details and ensures you have sufficient funds. - Authorisation:
Once verified, the bank holds this authorisation on record. - Automatic Payments:
On scheduled dates (e.g., monthly), the bank automatically debits the specified amount. - Notification:
You receive a confirmation (via SMS or email) whenever a transaction is processed.
This automation saves you time and ensures payments are made on time, a key fixture of modern digital finance.
Types of ECS Mandates
ECS mandates can be categorised in a few ways based on how and when they are triggered:
1. Fixed Amount Mandate
Used when the payment amount is the same each time, for example:
- Monthly utility bills
- Fixed EMI payments
2. Variable Amount Mandate
Used when the bill amount varies, for example:
- Credit card bills
- Monthly utility usage like electricity or water
3. Single Debit ECS
This mandate allows a one-time debit, useful for a single payment or settlement.
4. Repeated Debit ECS
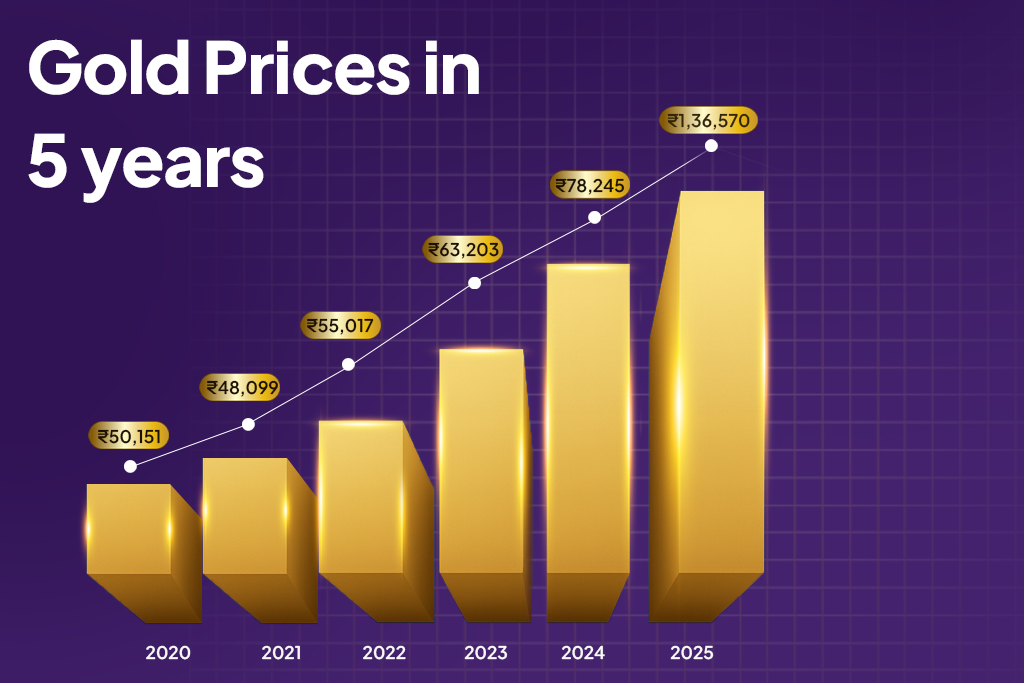
This allows multiple debits over time at regular intervals, ideal for subscriptions and recurring bills. You can also start digital gold investment regularly using a repeated debit ECS to build your gold portfolio gradually and effortlessly.
Understanding these types helps you choose the right mandate for your financial needs.
Benefits of ECS Mandate
Using an ECS mandate offers several advantages:
✔ Convenience
Once set up, payments are automatic, no manual fund transfers every month.
✔ Timely Payments
Prevents late or missed payments, which is especially important for EMIs, subscriptions, and insurance.
✔ Saves Time
No need to log in every month to initiate a transaction.
✔ Better Financial Planning
With regular automated deductions, it becomes easier to plan expenses and budgeting. You can also set up automated SIP via ECS mandate to invest consistently in mutual funds or ETFs without worrying about missing payments.
✔ Reduces Paperwork
Digital mandates reduce the need for cheques, cash, or standing instructions.
How to Set Up an ECS Mandate
Setting up an ECS mandate usually involves the following steps:
- Obtain the Mandate Form:
From your service provider, bank, or lender. - Fill in Details:
Provide your name, bank account number, amount, frequency, and duration. - Submit to Biller or Bank:
Hand over the signed form to the organisation you’re paying. - Bank Verification:
Your bank verifies the mandate and confirms it. - Activation:
Once activated, the recurring debit starts as scheduled.
Many providers now allow digital mandates where you can complete this process online without any paperwork.
How to Cancel or Modify an ECS Mandate
There may be times when you want to change or stop an ECS mandate:
- Inform the Biller:
Notify the organisation you authorised the mandate with. - Submit Cancellation/Modification Request:
Provide a written or digital request to either stop or change amounts/frequency. - Bank Updates Mandate:
The bank processes the change and confirms the action.
Always ensure cancellation or modification is completed before the next debit date to avoid unintended deductions.
ECS vs NACH
While ECS has been widely used for years, a newer system called NACH (National Automated Clearing House) has largely replaced traditional ECS mandates in India due to improved efficiency.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | ECS | NACH |
| Speed | Slower settlement | Faster, real-time processing |
| Reliability | Limited window for transactions | Higher success rate |
| Reconciliation | Manual reconciliation common | Automated and streamlined |
| Adoption | Older system still in use | Increasingly standard across banks |
| Error Handling | Prone to more failures | Lower failure rate |
While both systems automate recurring payments, NACH is more robust, quicker, and preferred by banks and large institutions today. However, the underlying concept of authorising automated debits remains similar.
FAQs
1. What is the ECS mandate?
An ECS mandate is an authorisation given by a bank account holder allowing automatic deductions from their account for recurring payments.
2. Is ECS the same as NACH?
No. ECS is the older system for automated payments, while NACH is its more efficient and widely used successor.
3. What types of ECS mandates exist?
There are fixed amount mandates, variable amount mandates, single debit, and repeated debit mandates.
4. Can I cancel an ECS mandate?
Yes. You can request cancellation or modification with your bank or the biller.
5. Why use an ECS mandate?
It ensures timely, automatic payments, helps with budgeting, and saves time on manual transactions.
Simplify Your Recurring Payments with FatakPay
Managing recurring expenses doesn’t have to be manual or stressful.
Explore how FatakPay helps streamline digital payments and improve your financial planning today!
To better understand key loan and repayment concepts related to ECS mandates, you may find these guides helpful:
- What is personal loan – Understand how personal loans work, their features, and how repayment methods like ECS are used.
| Personal Loans by City | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Loan Bengaluru | Personal Loan Thane | Personal Loan Mumbai | Personal Loan Hyderabad | |
| Personal Loan Pune | Personal Loan Surat | Personal Loan Coimbatore | Personal Loan Delhi | |
| Personal Loans by Amount | ₹60,000 Personal Loan | ₹3 Lakh Personal Loan | ₹5 Lakh Personal Loan |
|---|